As interest in the ketogenic diet continues to grow, a number of ketogenic supplements have emerged over the past few years. Leading the way in terms of fat fuel supply is a small compound known as beta-hydroxybutyric acid or BHB for short.
You may have heard a lot about BHB and the potential benefits it offers, but you may not be entirely sure what BHB is, where it comes from, or why it is included in supplements tailored specifically for ketogenic dieters.
This article will answer all of those questions and more.
So, let’s get started!
What Is Beta-Hydroxybutyrate (BHB)?
Beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) is an organic compound called a “ketone body” that is produced by the liver in a hypoglycemic or low-carbohydrate diet (e.g., a weight-loss diet).
BHB plays a number of important roles in the body. First, BHB can increase the body’s metabolic rate by supplying the energy needed to help people burn more fat and lose weight. Second, BHB can also help reduce inflammation and improve the body’s immune system function, and it can help lower blood sugar levels and improve cardiovascular health, among other things.
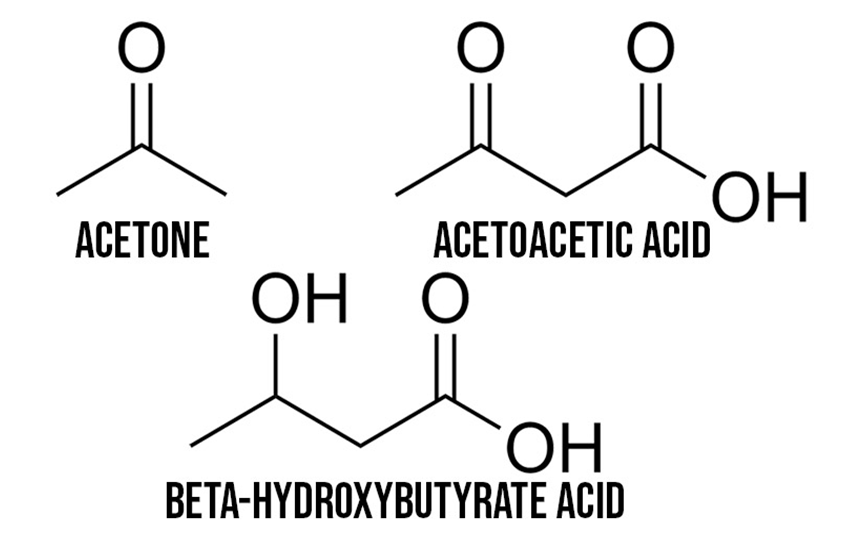
Basics of β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) production
BHB is produced through a process called ketogenesis (“origin of ketone bodies”).
When our body is in a state of fasting or glucose depletion (muscle and liver glycogen are also low), insulin levels drop. Low insulin levels allow the process of lipolysis to occur, which means that fat cells begin to release free fatty acids from our internal stores. These fatty acids are then sent to the liver and are broken down into a molecule called acetyl-CoA (acetyl-CoA).
In the liver, acetyl-CoA undergoes a series of steps that eventually lead to the production of the ketone body acetoacetate (AcAc).
An enzyme called BHB dehydrogenase converts AcAc to BHB, and once BHB is produced, specialized transport proteins transfer it from the liver to the circulation, where it is used as fuel. Using BHB as energy basically involves a process that reverses ketogenesis – acetyl coenzyme A is produced by the breakdown of BHB, which is then used to produce ATP.
How exactly does BHB move? It is transported from the liver via a transporter protein called the monocarboxylate transporter (MCT), not to be confused with MCT oil (short for medium-chain triglyceride oil).
Exogenous Ketones
So far, we have been discussing the body’s natural production of ketone bodies, also known as endogenous ketone bodies. Ketone bodies can also be supplemented in the form of BHB salts, molecules of BHB combined with minerals such as sodium, calcium or magnesium. When these are ingested, the body releases BHB for energy, while the minerals support a myriad of other bodily functions such as hydration, muscle function and blood clotting.
Now, you may be wondering why you still need to supplement with BHB salts if you are already following a ketogenic diet. Well, if a person is used to eating a very high carb diet and suddenly transitions to an ultra-low carb ketogenic diet, it may take some time for the body to adapt to producing sufficient amounts of ketone bodies to power its myriad of activities. As the body “rejuvenates”, flu-like symptoms (lethargy, brain fog, cramping, etc.) may occur. This condition is known as “keto-flu”.
People transitioning to a keto lifestyle can supplement with exogenous ketone bodies (in the form of BHB salts) to help ease the transition by providing the body with easily accessible fuel. This may reduce fatigue and speed up the body’s transition to burning fat for fuel.

How to increase Beta-Hydroxybutyrate levels
Of course, BHB production and ketosis used to be a “survival” mechanism activated by starvation. But that doesn’t mean we have to experience starvation to reap the benefits of BHB.
In fact, some lifestyle changes can raise your beta-hydroxybutyrate levels and put you into ketosis.
fasting
Typically, we have some BHB in our blood (even if you are not fasting or on a ketogenic diet), but its levels are barely detectable and too low to have any significant physiological impact.
After 12-16 hours of fasting, the ketone bodies in the blood rise slightly to a few hundred micromoles. After about two days of fasting, blood BHB rises to 1 mM-2 mM. Under more prolonged “starvation” conditions (6-8 days), blood BHB levels may be in the range of 6 mM-8 mM.
Exercise
Don’t want to restrict your food intake? Fortunately, there is a way into ketosis that doesn’t necessarily require eating a no-carb diet or prolonged fasting.
Post-exercise ketosis can occur for a variety of reasons, which may include: depletion of glucose and glycogen during exercise; elevated circulating free fatty acids released during exercise; and hormonal changes that regulate ketogenesis.
Ketogenic Diet
BHB can also be increased by consuming a diet high in fat and low in carbohydrates (also known as a ketogenic or “ketogenic” diet). In fact, restricting carbohydrate intake is one of the most effective ways to increase blood ketone levels and induce nutritional ketosis.
In addition, a ketogenic diet is a way to consistently increase ketone levels over time, as opposed to short-term fasting and exercise. If you want to “live in ketosis”, a carbohydrate-restricted diet is the way to go.
Where can I find Beta-Hydroxybutyrate (BHB)?
Premium Blast Keto ACV Gummies is an advanced weight loss formula, a proprietary form of exogenous ketone salts that supports healthy metabolism, increased energy and fat burning.
Learn more about Premium Blast Keto ACV Gummies and how it can help you achieve your weight loss goals.




